Buzzer Interfacing with 8051 Microcontroller | Circuit Diagram & Program
Introduction
Buzzer interfacing with 8051 microcontroller is a fundamental concept in embedded systems and microcontroller-based projects. Buzzers are commonly used to generate audio alerts and warning signals in electronic devices such as alarm systems, security systems, and automation projects.
In this tutorial, you will learn how to interface a buzzer with the 8051 microcontroller (AT89C51), including circuit diagram, working principle, algorithm, and Embedded C program. This guide is highly useful for engineering students, diploma students, and beginners preparing for 8051 practicals and project work.
What is a Buzzer?
A buzzer is an electronic audio signaling device that converts electrical energy into sound energy. It is widely used to provide alert indications in embedded and electronic systems.
Types of Buzzers Used in Embedded Systems
Active Buzzer – Produces sound when powered (no external frequency needed)
Passive Buzzer – Requires an external square wave or PWM signal
👉 Active buzzers are mostly used with 8051 microcontroller projects due to their ease of interfacing.
Why Interface a Buzzer with 8051 Microcontroller?
Interfacing a buzzer with 8051 helps in:
Generating audio alerts
Indicating system errors or status
Creating alarm and warning systems
Understanding digital output control
Common 8051 Buzzer Applications
Fire alarm systems
Temperature monitoring systems
Security and intrusion alarms
Electronic voting machines
Home automation projects
Components Required for Buzzer Interfacing with 8051
To build a buzzer interfacing circuit using 8051 microcontroller, the following components are required:
AT89C51 / AT89S52 Microcontroller
Active Buzzer (5V)
Resistor (220Ω – optional)
5V Power Supply
Breadboard and jumper wires
8051 Microcontroller Pin Configuration
The 8051 microcontroller consists of four I/O ports:
Port 0
Port 1
Port 2
Port 3
For buzzer interfacing, Port 1 or Port 2 is recommended because of built-in pull-up resistors.
Pin Connection Example
Buzzer positive terminal → P1.0
Buzzer negative terminal → GND
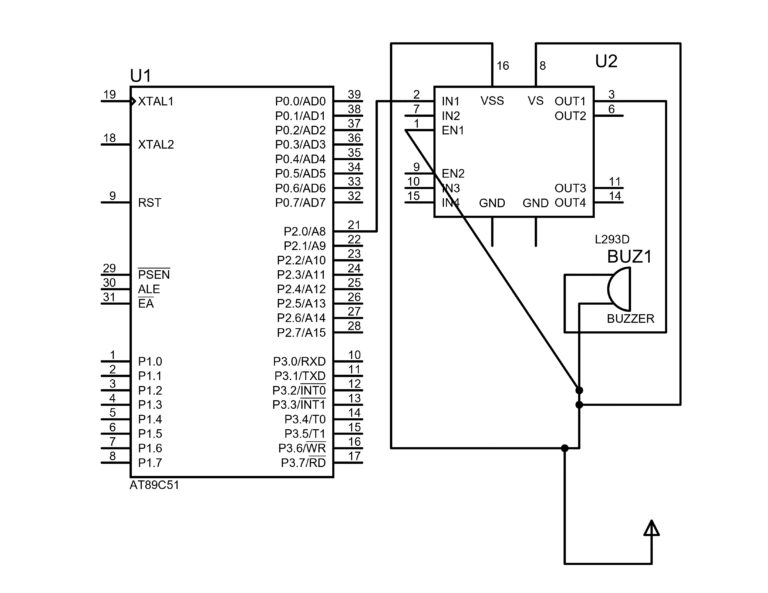
Circuit Diagram for Buzzer Interfacing with 8051 Microcontroller
📌 Circuit Explanation:
The buzzer is connected to P1.0 of the 8051 microcontroller
When the port pin goes HIGH, the buzzer turns ON
When the port pin goes LOW, the buzzer turns OFF
Working Principle of Buzzer Interfacing with 8051
The working principle is based on digital output control:
Microcontroller sends logic HIGH to the buzzer pin
Current flows through the buzzer
Sound is generated
Logic LOW stops the current and buzzer turns OFF
By controlling ON-OFF timing using software delays, different beeping patterns can be generated.
Algorithm for Buzzer Interfacing Program
Start the program
Configure buzzer pin as output
Turn ON the buzzer
Provide delay
Turn OFF the buzzer
Provide delay
Repeat continuously
Embedded C Program for Buzzer Interfacing with 8051 Microcontroller
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elit tellus, luctus nec ullamcorper mattis, pulvinar dapibus leo.
Click Below: To Download Complete Proteus Circuit Design and Hex File
Applications of Buzzer Interfacing with 8051 Microcontroller
Alarm and warning systems
Industrial fault indication
Embedded training projects
Educational demonstrations
Automation systems
Advantages of Using Buzzer with 8051
Simple hardware interfacing
Low power consumption
Cost-effective solution
Easy to program
Ideal for beginners
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
❓ Which port is best for buzzer interfacing in 8051?
Port 1 is best because it has internal pull-up resistors.
❓ Can a passive buzzer be used with 8051?
Yes, but it requires a square wave or PWM signal from the microcontroller.
❓ What voltage does a buzzer need?
Most active buzzers operate at 5V, suitable for 8051.
❓ Is a transistor required for buzzer interfacing?
For small buzzers, direct connection is fine. For high-power buzzers, use a transistor driver.
Conclusion
Buzzer interfacing with 8051 microcontroller (AT89C51) is a beginner-friendly and essential embedded systems experiment. It helps students understand I/O port control, hardware interfacing, and real-time alert generation. This project is widely used in academic labs, mini projects, and real-world applications.